Severe drought conditions that plagued California one month ago diminished in parts of the state due in part to a series of early winter storms, this week's U.S. Drought Monitor report shows.
Most of California, except for the extreme northwest corner, remains is some level of drought this week, but conditions improved significantly in the most severe categories. The weekly report released Thursday shows exceptional drought was nearly erased after 28 percent of the state was under the most severe category in the first week of December.
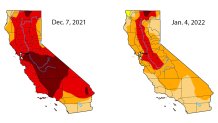
About 16 percent of the state -- a swath in the north-central region -- is in extreme drought, down from 33 percent last week and 80 percent in early December. Three months ago, that figure was at 88 percent.
Get a weekly recap of the latest San Francisco Bay Area housing news. Sign up for NBC Bay Area’s Housing Deconstructed newsletter.
The storms fueled by a band of moisture over the Pacific began the week of Christmas and continued to usher in rain and mountain snow for days. During those two weeks of steady rain and snow, precipitation averaged 150 to 300 percent of normal or more throughout nearly all of California.
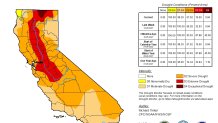
"In what has become a familiar pattern, heavy precipitation continued to improve drought and dryness across the northern half of the West Coast States, though it created its own set of significant impacts," this week's report summary said. "Farther south, similar totals fell on a relatively small area in southwest California."
California's mountain snow holds 160% of the water it normally does this time of year, state water officials announced in late December.
"Heavy precipitation and a generous snowpack in mountainous areas led to more improvement here, based in part on monthly statistics for December," according to the report. "Improvement was brought into large swaths of the region, especially across central Montana, much of Idaho and Utah, western Nevada, and part of central and southern California."
Photos: December Storm Images From Around California
Droughts are common in California, where dry spells are often followed by wet winters that replenish the state's critical snowpack and water reservoirs. And it takes more than a lot of rain and snow in one shot to ease drought conditions.
The state is “definitely not out of the woods quite yet," said Sean de Guzman, manager of the snow surveys and water supply forecasting for the California Department of Water Resources.
Prolonged hot and dry conditions over moths and years means water evaporates at a faster rate from reservoirs and the Sierra Nevada snowpack that feeds them. The snowpack usually melts in spring or early summer, then that water flows into the state’s vast storage and distribution system.
About a third of California's water supply comes from snow as it melts and flows down from the Sierra Nevada and the Shasta-Trinity mountain range in northern California.
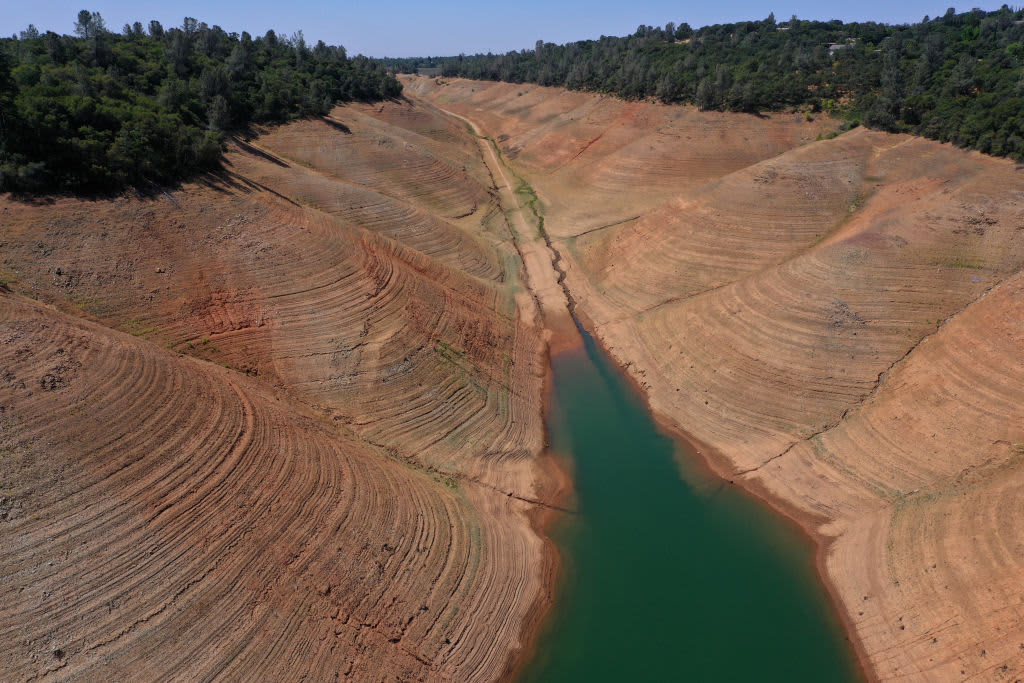
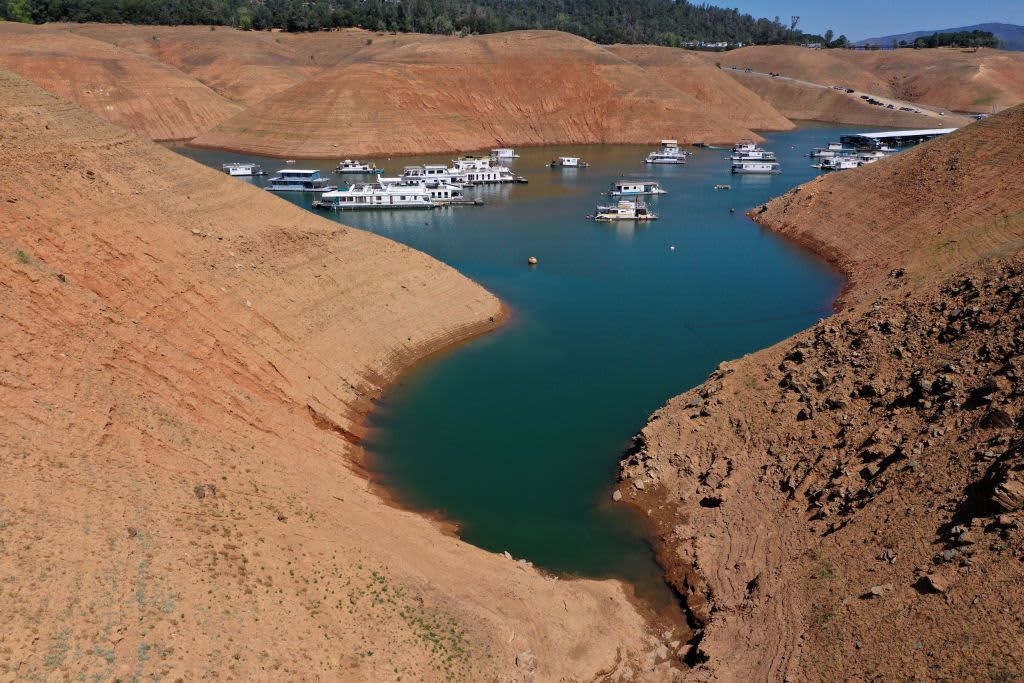
California has more than 500 reservoirs, which were 50% lower than they should be at the start of June. These photos show the dramatic impact of the current dry spell at California’s lakes and reservoirs.
California's Mediterranean-style climate means the summers are always dry and the winters are not always wet. The state's reservoirs act as a savings account, storing water in the wet years to help the state survive during the dry ones.
Last year was the third driest on record in terms of precipitation.
Drought is generally defined as a period of drier-than-normal conditions resulting in water-related problems. That period can be days, weeks, months and years.
The term can have different meanings, depending on how water users are affected by water deficiencies. In a state of 40 million people, that's a lot of water users impacted in different ways by dry spells.
Droughts have been classified into the following:
- Meteorological drought means a lack of precipitation.
- Agricultural drought describes a lack of soil moisture.
- Hydrologic drought indicates reduced streamflow or groundwater levels.
California recently went through a five-year event from 2012-2016. Other notable historical droughts included 2007-09, 1987-92, 1976-77, and off-and-on dry spells of more than a decade in the 1920s and 1930s.



